- April 22, 2025
Ultrasonic pulse velocity test
Ultrasonic pulse velocity test is performed on concrete to check their quality and homogeneity and also cracks, voids, cavities and defects in the concrete by passing electronic wave through the concrete. The apparatus used in the test is called ultrasonic pulse velocity meter.

Testing of Concrete Cores for Strength

Rebound Hammer Test
Rebound Hammer test is a Non-destructive testing method of concrete which provide a convenient and rapid indication of the compressive strength of the concrete. The rebound hammer is also called as Schmidt hammer that consist of a spring controlled mass that slides on a plunger within a tubular housing. When the plunger of rebound hammer is pressed against the surface of concrete, a spring controlled mass with a constant energy is made to hit concrete surface to rebound back. The extent of rebound, which is a measure of surface hardness, is measured on a graduated scale. This measured value is designated as Rebound Number (rebound index). A concrete with low strength and low stiffness will absorb more energy to yield in a lower rebound value.
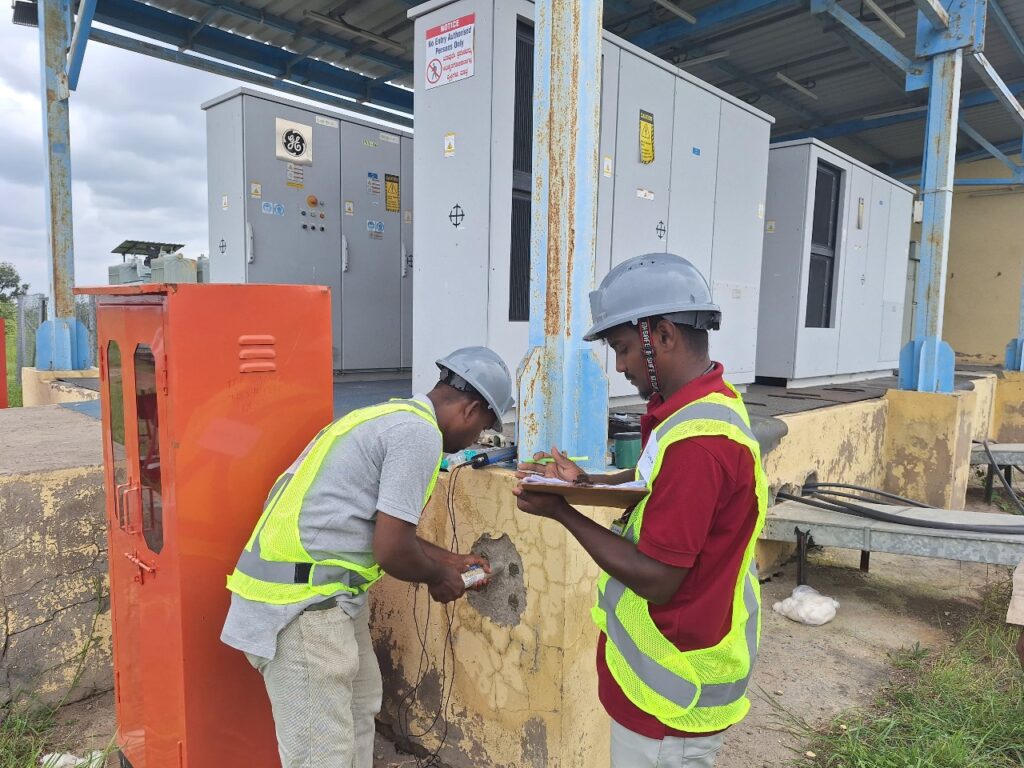

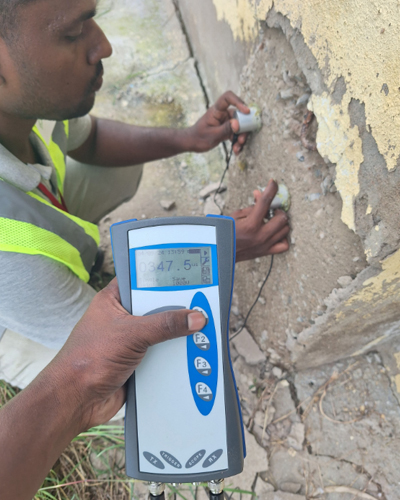
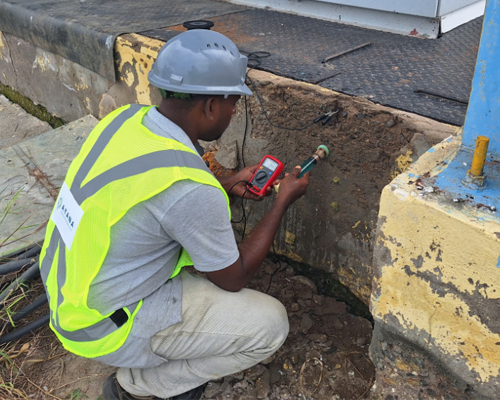
Half-cell Potential Test
The half-cell potential test is the only corrosion monitoring technique standardized in ASTM C876 – 15: Standard Test Method for Corrosion Potentials of Uncoated Reinforcing Steel in Concrete. It is used to determine the probability of corrosion within the rebar in reinforced concrete structures.

Rebar Scanning
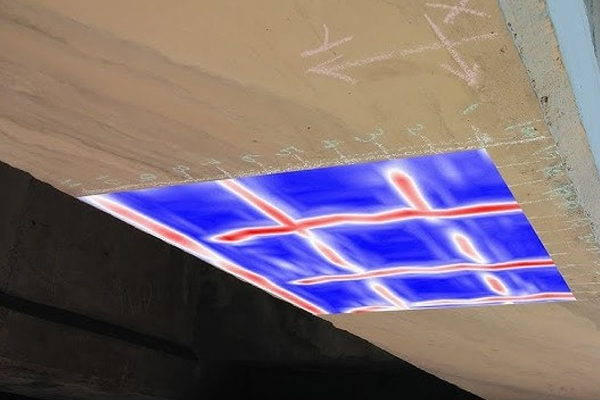
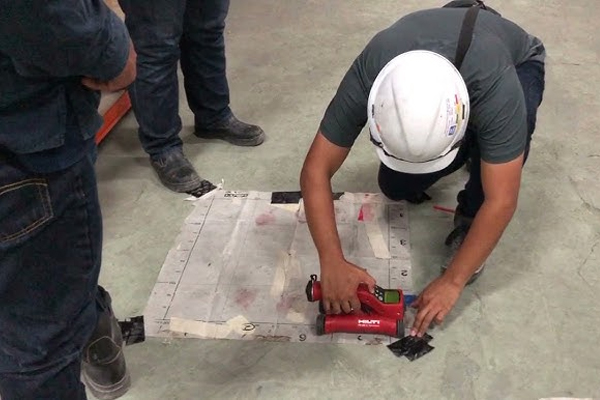
Rebar scanning is a non-destructive testing (NDT) method used to locate and assess the spacing & diameter of reinforcing steel (rebar) within concrete structures. It helps determine the rebar’s location, depth & diameter. This is crucial for structural integrity assessment, preventing damage during drilling or coring, and ensuring the quality of concrete construction.
Rebar scanning helps engineers and contractors locate rebars within RCC structures before drilling or coring, and assess the structural integrity.